Network Modeling
Advancing network-level tools for analyzing sustainability, equity, and resilience across multimodal transportation systems.
Background
Traditional asset-level approaches are often constrained in assessing the sustainability and equity of multimodal transportation systems. At the network level, emerging properties such as cumulative exposure to pollutants and extreme temperature, cascading failures during disruptions, and tipping points leading to system breakdowns become critical. Despite growing attention to connectivity in transportation networks, many tools used in practice still focus narrowly on individual assets.
Framework and Applications
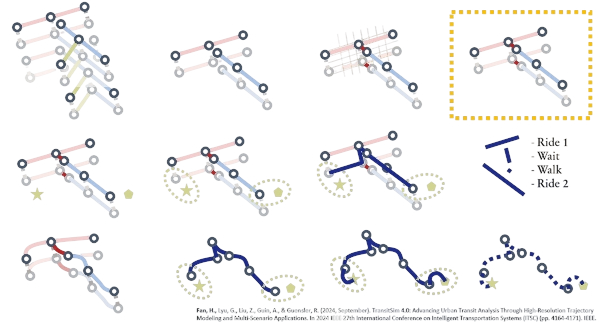
Multimodal Network Simulation
We simulate second-by-second travel behavior across buses, walking, cycling, and shared mobility systems to quantify accessibility and exposure.
Tool Integration
Our simulation tools integrate seamlessly with travel demand models, enabling network-scale scenario testing for equity, energy, and emissions outcomes.
Applications in Practice
These tools have been used to evaluate bus fleet electrification, transit service changes during COVID-19, carpooling strategies, and freight emissions.
Ongoing Work
We are working to integrate multimodal interactions into our toolkits, optimize for large-scale simulations, and develop user-friendly resources for planners. Looking ahead, we aim to expand this platform to compare energy and emissions pathways, assess health impacts, and evaluate resilience strategies. Our long-term goal is to provide comprehensive, open-access modeling tools for both researchers and agencies.
Join Us
If you're a prospective student interested in pursuing research related to this topic, please visit this page for the latest updates on graduate opportunities. When completing your application, be sure to type "[Network Modeling]" in response to the question: "If there are any special circumstances that you'd like me to know about, please list them here." (If there are actual circumstances to share, feel free to elaborate after the square brackets).
Related Publications
- Fan, H., Lyu, G., Liu, Z., Guin, A., & Guensler, R. (2024, September). TransitSim 4.0: Advancing urban transit analysis through high-resolution trajectory modeling and multi-scenario applications. In 2024 IEEE 27th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC) (pp. 4164–4171). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITSC58415.2024.10919702
- Fan, H., Lu, H., Guin, A., & Guensler, R. (2024). Using multi-modal path-specific transit trips in transportation social sustainability analysis: Case study in Atlanta, GA. https://doi.org/10.7922/G2HH6HD0
- Fan, H., Lu, H., Dai, Z., Passmore, R., Guin, A., Watkins, K., & Guensler, R. (2023). Combined effect of changes in transit service and changes in occupancy on per-passenger energy consumption. Transportation Research Record, 2677(2), 1252–1265. https://doi.org/10.1177/03611981221111160
- Lyu, G., Fan, H., Lu, H., Tennakoon, M., Bhosale, K., Hawkins, M. R., & Guensler, R. (2024, February). Electrification opportunities and challenges of school bus transportation: A case study of Atlanta Public Schools. In 2024 Forum for Innovative Sustainable Transportation Systems (FISTS) (pp. 1–7). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/FISTS60717.2024.10485608
- Fan, H., Lu, H., Gomez, E., Costa, S., & Guensler, R. (2024, February). Well-to-wheel energy use and emissions impacts of conventional and alternative fuels on delivery of live clams to Atlanta Metro Area: Diesel vs. battery electric from solar. In 2024 Forum for Innovative Sustainable Transportation Systems (FISTS) (pp. 1–8). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/FISTS60717.2024.10485595
